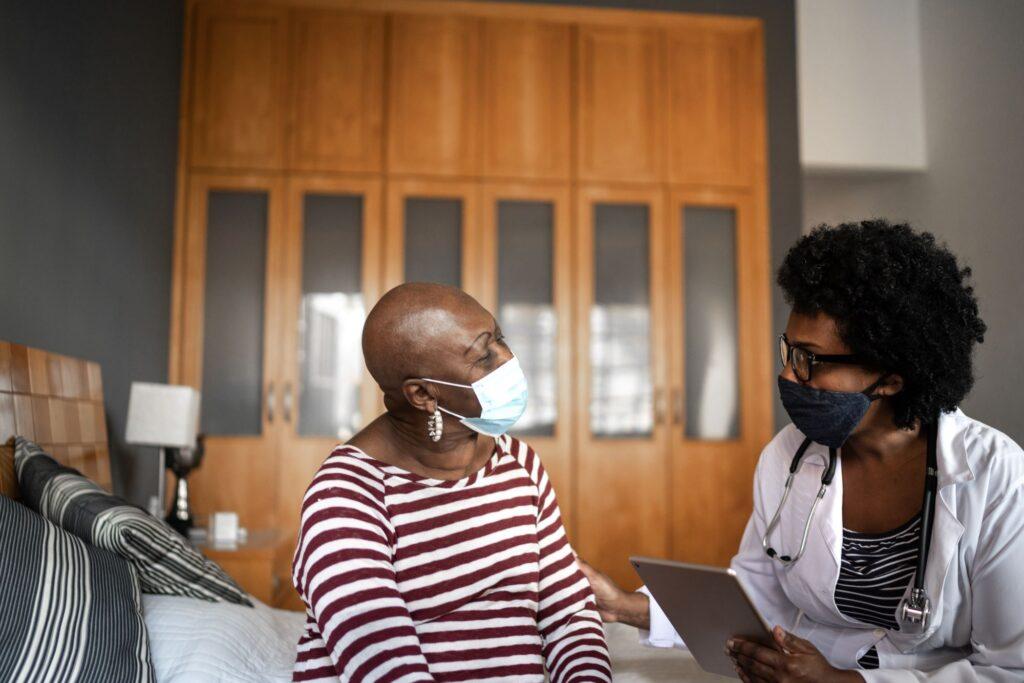
Providing equitable health care remains a pressing issue in many societies, particularly among historically marginalized populations. In recent years, there has been an increasing recognition of the critical role that Black medical professionals play in serving Black communities. Providing culturally competent care and understanding the unique health disparities that Black individuals face is essential for addressing health care inequities. Here, let’s explore the significance of the representation, trust, cultural sensitivity, and improved health outcomes that arise from increasing the presence of Black health care professionals within the medical field. These realities underscore the importance of Black medical professionals in promoting diversity, equity, inclusion, and justice (DEIJ) within health care systems.
The Historical Context of Health Care Inequities
Understanding the significance of Black medical professionals requires acknowledging the historical context of health care inequities within the Black community. Racial disparities in health care have persisted for decades, leading to disproportionate rates of certain diseases, higher mortality rates, and distrust within the Black community toward the medical system. According to a report by the Government Accountability Office (GAO), the maternal death rate for Black or African American women was 44.0 per 100,000 live births in 2019. This rate increased to 55.3 in 2020 and climbed to 68.9 in 2021. In contrast, white women had significantly lower death rates of 17.9, 19.1, and 26.1 during the same respective years.
In terms of COVID-19, there are significant racial disparities in outcomes among Black individuals. Studies have shown that Black patients have experienced higher rates of hospitalization and death due to COVID-19 compared to white patients. Regarding death rates, the CDC has reported that the death rate for African Americans/Blacks in the United States is higher compared to other racial/ethnic groups. In 2018, the death rate for African Americans/Blacks was 16.3 per 100,000, while it was only 2.5 per 100,000 for whites. It is essential to address these health disparities and work toward implementing policies and interventions that promote health equity for the Black community.
Role of Black Medical Professionals: Social Justice Perspective
From a social justice perspective, having Black medical professionals in Black communities is vital in addressing systemic health disparities. Historically, Black communities have faced more significant barriers to accessing quality health care due to various factors such as lack of insurance, limited resources, and discrimination. These disparities have had detrimental effects on the overall health and well-being of Black individuals and contribute to the racial health inequities that persist today.
There are several significant benefits to increasing the representation of Black medical professionals:
- Cultural Sensitivity and Understanding. Black medical professionals better understand the cultural nuances, experiences, and challenges Black individuals face. They can provide more culturally sensitive care, which can help build trust and improve patient-provider communication. Furthermore, representation plays an influential role in shaping health care experiences.
- Enhanced Access to Care. Black medical professionals can serve as role models and mentors, inspiring young people in the community to pursue careers in health care. As a result, there will be a greater likelihood of Black individuals seeking medical care and receiving appropriate treatment. Such representation promotes diversity and helps cultivate a more inclusive environment where patients feel understood, respected, and empowered.
- Building Trust. The historical mistreatment of Black individuals in medical settings has led to deep-rooted mistrust. Including Black doctors, nurses, and other health care professionals helps foster trust between minoritized patients and their providers. Patients who relate to and identify with their health care providers are more likely to communicate openly, share relevant medical information, and actively participate in decision-making. Trust ultimately leads to better health outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
- Addressing Implicit Bias. Black medical professionals can help combat the implicit biases in health care. Studies have shown that medical professionals from different racial backgrounds may have different biases and treatment approaches. Having Black professionals in the field can help challenge and mitigate unconscious biases that may negatively impact Black patients.
- Tailored Health Care Strategies. Black medical professionals can help develop and implement health care strategies that specifically address Black communities’ unique health challenges. They are better positioned to advocate for policies and interventions that consider the social determinants of health and address the root causes of health disparities.
- Community Engagement. Black medical professionals can play an active role in community engagement and education, promoting preventive care, conducting health screenings, and addressing health concerns specific to the community. This engagement can help empower individuals and communities to take charge of their health.
Final Thoughts
Diverse representation in the medical profession is necessary to address health care disparities and promote equity in Black communities. Through their presence, Black medical professionals serve as catalysts for change, advocating for improved health care policies, fostering trust, providing culturally sensitive care, and ultimately contributing to better health outcomes. Health care institutions and policymakers must make concerted efforts to recruit, retain, and support Black medical professionals, ensuring they play a central role in shaping a more inclusive and equitable health care system for all.